The Russian Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS) is a GNSS satellite navigation system developed as an alternative, as well as complementary to other satellite systems such as the United States’ Global Positioning System Navstar (GPS), the Chinese BeiDou-3 navigation system or the European Union Galileo Positioning System (Galileo).
The main use of of the system at the time was as an experimental military communications system.
Russia commenced the development of the GLONASS system in 1976, and by 1982 the first satellite had been deployed, with the constellation becoming fully operational in 1995.
GLONASS provides real time position, velocity location data for both military and civilian use.
Orbitital Plane
The satellites are located in orbit at a height of around 19,100km, with an inclination of 64.8°.
To complete a full orbit, the duration in which it takes is of 11 hours and 15 minutes.
The orbit of GLONASS’s is perfectly set u for usage in higher latitudes in both Northern and Southern, where GPS signal has known to be problematic.
The satellite constellation operates at three planes of orbit, with eight satellites spaced evenly apart within their plane.
The fully operational GLONASS constellation consists of 24 satellites, whilst to cover Russia only 18 are required.
Versions of GLONASS
Original satellites released in 1982 for military and official state use. These satellites were intended for timing, weather, velocity and navigational measurements.
- Release date: 1982
- Phase: Completed
GLONASS-M
These satellites were launched in 2003 to add second civil code, which is important for GIS mapping receivers.
GLONASS-K
There are 3 types of this satellite, which are K1, K2 and KM, operating in the third civil frequency.
- Release Date: 2011
- Phase: Completed
GLONASS-K2
These satellites will be launched after 2015 (currently in design phase).
- Release Date: 2015
- Phase: Design
GLONASS-KM
- Release date: After 2025
- Phase: Research
Services
The two services that are available from GLONASS system are as follows
SPS: The Standard Accuracy Service
The Standard Accuracy Service (or Standard Positioning Signal service) is an a service that is free of charge for worldwide users.
Initially the navigational signals were only provided in the G1 frequency band, but as of 2004 the GLONASS-M satellite transmits in the G2 civil frequency,
PPS: The Precise Positioning Service
The Prcise Positioning Service, also known as High Accuracy Signal service is restricted to military and authorized users only.
Frequency bands G1 and G2 are the where the navigation signals are serviced.
Ground Control Segment
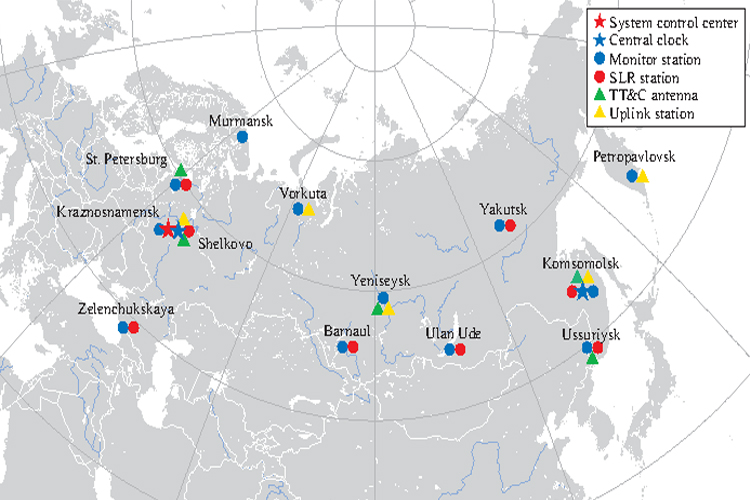
The entirety of the GLONASS ground control segment of is located within former Soviet Union territory.
The Time Standards and Ground Control Center is located in Moscow, whilst the tracking and telemetry stations are in Eniseisk, Komsomolsk-na-Amure, Saint Petersburg and Ternopol.
GLONASS constellation is managed by System Control Center (SCC).
GLONASS Network
SCC:System Control Center
TT&C:Telemetry, Tracking and Control
ULS:Uplink station
MS:Monitoring station
CC:Central clock
SLR:Laser tracking station