Geocoding, or address geocoding, is the conversion process of text-based location description, and returning latitude & longitude co-ordinates.
The most common text-based location description would be an address.
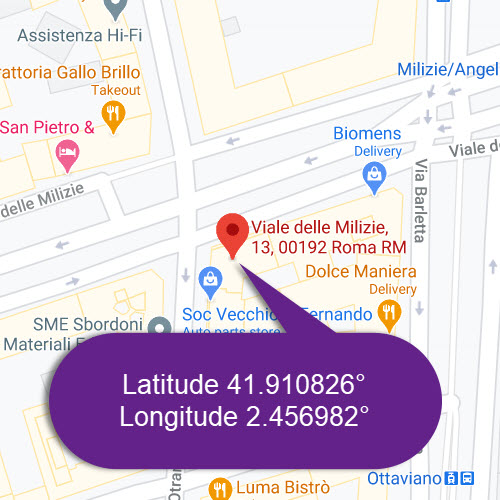
An example of the geocoding process would take the address 13 Viale Delle Milizie, Rome, Italy, and then proceed to convert it to Latitude 41.910826°, Longitude 12.456982°
The uses of geocoding
Geocoding is used in gps tracking software, as a way to create and store human-readable data.
In addition, geocoding can be used for simple analysis of data to customer and business management, right through to to distribution techniques.
With addresses that are geocoded, you can display the address locations spatially and determine patterns from analyzing the information.
This can be achieved by using software analysis tools, such as GIS mapping software.
Geocoding process
- Every geocoding tasks begins with the input data.
This data is the list of addresses that require geocoding.
Users or automated systems start the process of geocoding by inputting this data set. - The Input data is then classified into either absolute input data or relative input data.
i.) Relative Input Data
Example: The white two story house next door to us.
This data is too vague to geocode.
ii.) Absolute Input Data
Example: 13 Viale Delle Milizie, Rome, Italy
This data can be split up into street number, name, city, country and is a perfect candidate for geocoding. - Absolute Input data is then geocoded and turned into a list of co-ordinates; latitude & longitude.
Concerns for privacy
The increase and ease of access to services that provide geocoding and reverse geocoding raises some valid concerns regarding privacy.
An example of this is with criminal activity.
Law enforcement attempts to balance the rights to privacy for victims and offenders, whilst considering the public’s right to know.
Agencies have attempted alternate geocoding processes which provides the ability to obscure portions of locational details.
An example of this would be to obscure a victim or offenders address.
In addition to providing online crime mapping to the public, agencies also place disclaimers in regards to the locational accuracy of certain points on the map, as well as imposing terms of use for the information.
Conclusion
Geocoded locations are used in many GIS analysis software, cartography functions, decision making workflows, transaction mash-ups, or utilized in larger business processes.
Online, geocoding is used in many services like local search and routing. Geocoding used in conjunction with GPS provides location data for media geotagging, such as photos and videos.
